
Of peroneus brevis the resultant biomechanical stresses lead to collapse of In abnormal loading of the transverse tarsal joints along with unopposed action The underlying causeĬan be varied risk factors include inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis,ĭiabetes mellitus, steroid use or overloading of the arch from obesity or Fixed bony deformity can occur at laterĬommon in females and often presents in the sixth decade. Tenosynovitis can progress to significant tendinosis with an incompetent and Zone of relative hypovascularity this is thought to contribute to degenerative However, there is an area of tendon distal to the medial malleolus,Īpproximately 2cm to 6cm from the attachment to the navicular, where there is a Tibial tendon receives its blood supply from branches of the posterior tibialĪrtery.

(PTTD) is becoming increasingly recognised as the main causative factor leading Underlying aetiology is multifactorial posterior tibial tendon dysfunction Incompetence or rupture of this ligament can cause or contribute to increasing

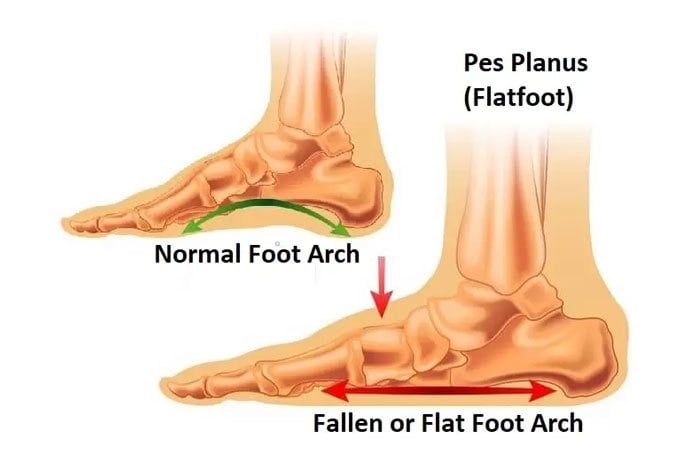
It is the primary static stabiliser of the talo-navicular joint. The sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus forward to the tuberosity of the The maintenance of the medial longitudinal arch is the plantarĬalcaneo-navicular, or spring ligament. Following inversion, the axes of the talonavicular andĬalcaneocuboid joints become non-parallel to allow the foot to become a rigidĬonstruct during the heel-rise and toe-off phases of gait. Subtalar joint this occurs following the foot-flat portion of the stance phase Plantar flexion of the ankle and initiation of inversion of the hindfoot at the Finally, a posterior division inserts onto sustentaculum tali anteriorly (Figure 1). A second division attaches the plantar surfaces of the middle and lateral cuneiforms, as well as the cuboid and the bases of the second to fifth metatarsals. The anterior division of the tendon inserts onto the navicular tuberosity, the medial naviculo-cuneiform joint capsule and the inferior surface of the medial cuneiform. It passes distally, anterior to the tuberosity of the navicular, where it divides. The posterior tibial tendon then runs at an acute angle behind the medial malleolus in a fibro-osseous groove, encased in a teno-synovial sheath. It is located in the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg and is innervated by the posterior tibial nerve (Figure 1). The posterior tibial muscle takes its origin from the posterior aspect of the proximal tibia, fibula and interosseous membrane. The development of adult acquired flat foot, the most common of these is theĭysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. There are several factors associated with Important in order to initiate appropriate management. Early recognition and diagnosis is therefore However, symptomatic patients can have severe pain and instability It is occasionally an asymptomatic incidental finding on clinicalĮxamination.

It can be defined as partial orĬomplete loss or collapse of the medial longitudinal arch.Īdult acquired flat foot can have a varied Literature looking at this relatively common deformityĪcquired flat foot is a relatively commonĭeformity encountered in the adult population. Killen, Rajiv Limaye and Neil Limaye conduct a brief review of the


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
